Architecture
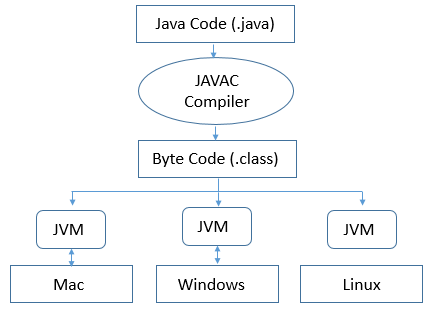
Data types
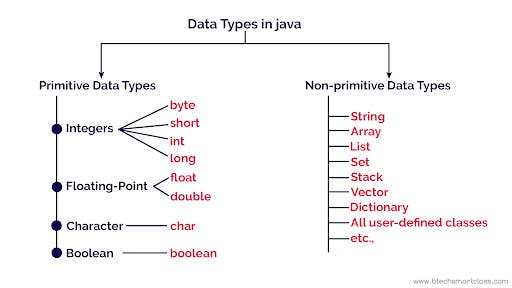
Control statement
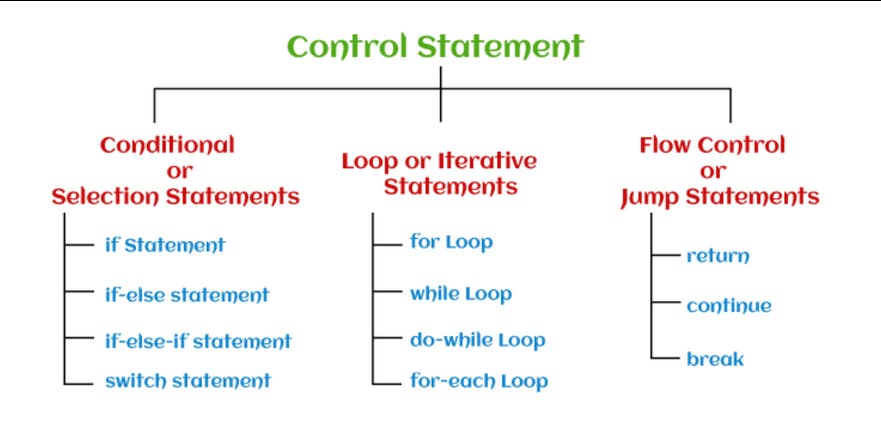
Flowchart
while loop
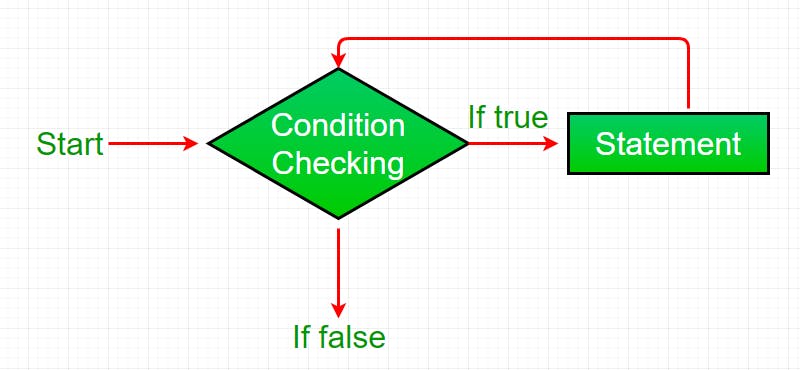
public class WhileLoopDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i < 6) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
i++;
}
}
}
Output
Hello 1
Hello 2
Hello 3
Hello 4
Hello 5
for loop
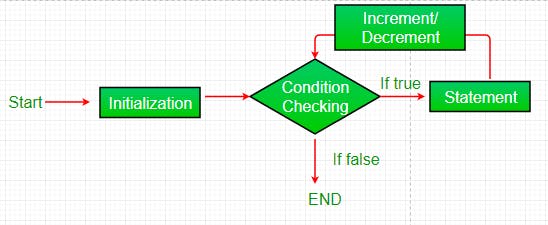
public class ForLoopDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("Hello " + i);
}
}
}
output
Hello 1
Hello 2
Hello 3
Hello 4
Hello 5
if else
public class IfelseLoopDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value = 5;
if (value == 5) {
System.out.println("value is eq = 5");
} else {
System.out.println("value is not eq = 5");
}
}
}
output
value is eq = 5
Break
The
breakstatement is used to terminate a loop early. When encountered inside a loop, it immediately exits the loop, skipping any remaining iterations.Example: Printing numbers from 0 to 9, but stopping when the value is 5
public class BreakExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i == 5)
break;
System.out.println("i: " + i);
}
System.out.println("Out of Loop");
}
}
output:
i: 0
i: 1
i: 2
i: 3
i: 4
Out of Loop
continue
The
continuestatement is used to skip the current iteration of a loop and proceed to the next iteration.Example: Printing numbers from 0 to 9, but skipping the value 4
public class ContinueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (i == 4)
continue;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
output
0
1
2
3
5
6
7
8
9
Debugging in java
- it's very important to solve/find the error in your code.
How to Debug
set
BreakpointsDebug as
step over (F6)
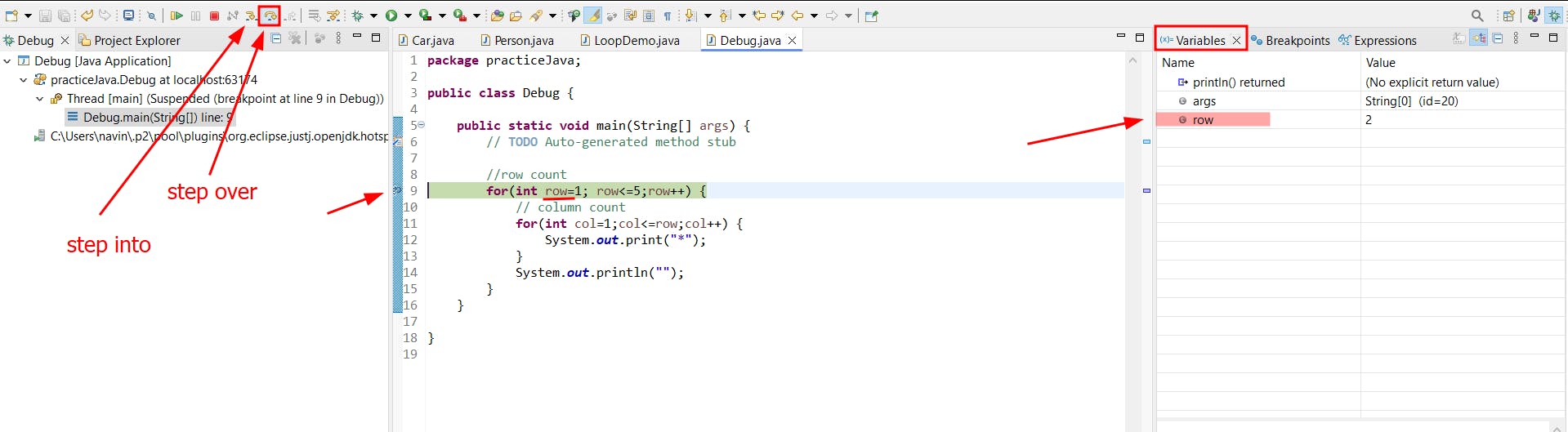
note: before i have used println so that i didn't get expected output. after debugging i find this. and changed to print
step over: executes the current line of code without entering method calls.
step into: enters the method call and executes its code line by line.
Arrays
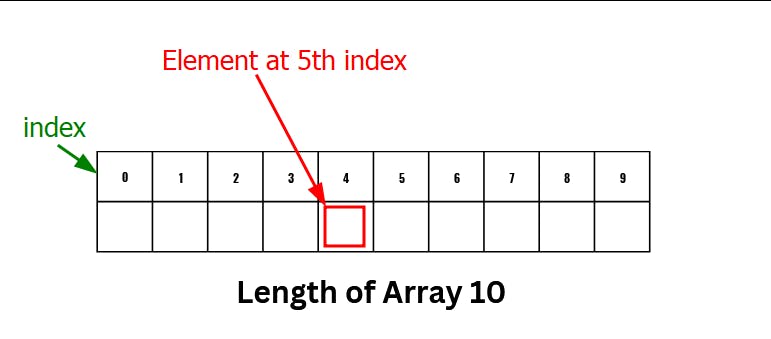
int[] arr={10,20,30,40};
// access the element
System.out.println("Element at 4th place"+arr[3]);
Methods
A method is a block of code which only runs when it is called.
You can pass data, known as parameters, into a method.
public class MethodDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// method call
int res = sumOfTwoNum(10, 5);
System.out.println(res);
}
// method creation
public static int sumOfTwoNum(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
static - means that the method belongs to the Main class (no need to create object for this)
not a problem if you not understand this keyword, you will understand this in next part of this java series.